Ever dreamt of navigating the exciting world of Forex trading (foreign exchange market), but worried about risking your hard-earned cash? Well, fret no more! This guide unlocks the secrets to start trading forex without any initial investment.
That’s right, you can learn the ropes of currency trading (currency pairs like EUR/USD, USD/JPY) and develop valuable skills, all without putting a single dollar on the line. We’ll explore how to leverage powerful tools like demo accounts and free educational resources to transform yourself into a confident forex trader (retail trader). So, buckle up and get ready to embark on your journey to mastering the forex market (financial markets and retail trading)!
Forex Trading Basics
The foreign exchange market, or forex market (also known as forex), is the world’s largest financial marketplace. It’s a global marketplace where individuals (retail traders), financial institutions, and even countries can trade currencies. Unlike stock exchanges, or other financial markets, forex isn’t a centralized location but rather a global network of banks, brokers, and individual traders electronically connecting to buy and sell currencies.
This guide dives into the core concepts of forex trading, providing a foundation for those interested in learning how to trade on forex.
Learn how the forex market works
In forex, currencies are always traded in pairs, representing the exchange rate between two currencies. For instance, EUR/USD signifies the Euro (EUR) relative to the US Dollar (USD). The first currency in the forex pair (EUR) is called the base currency, and the second (USD) is the quote currency. When you trade forex, you’re essentially buying or selling one currency in exchange for another, hoping to profit from future price movements in the chosen currency pair.
What Moves the Forex Market

Several factors influence currency values, impacting the forex market. Here are some key drivers:
Interest Rates: Central banks set interest rates, influencing borrowing costs and currency attractiveness. Higher interest rates tend to strengthen a currency.
Economic Growth: A strong economy fosters confidence in a nation’s currency. Conversely, a weak economy can lead to depreciation.
Geopolitical Events: Political instability or global conflicts can cause currency fluctuations due to risk perception.
Supply & Demand: Just like any market, currency values respond to supply and demand. Increased demand for a currency strengthens its value, and vice versa.
How Currencies Are Traded?

Forex trading involves buying and selling currency pairs. A currency pair represents the exchange rate between two currencies, like EUR/USD (Euro vs. US Dollar). Here’s the basic concept:
Buying a Currency Pair (Long Position): You believe the base currency (first currency in the currency pair’s price move) will strengthen against the counter currency (second currency). You aim to buy low and sell high for a profit.
Selling a Currency Pair (Short Position): You anticipate the base currency will weaken compared to the counter currency. You profit by selling your currency prices at high and repurchasing later at a lower price.
Types of Forex Markets (Spot & Forward)
The foreign exchange market offers different ways to trade currencies depending on your needs and risk tolerance. Here’s a breakdown of two prominent market types:
1. Spot Forex Market:
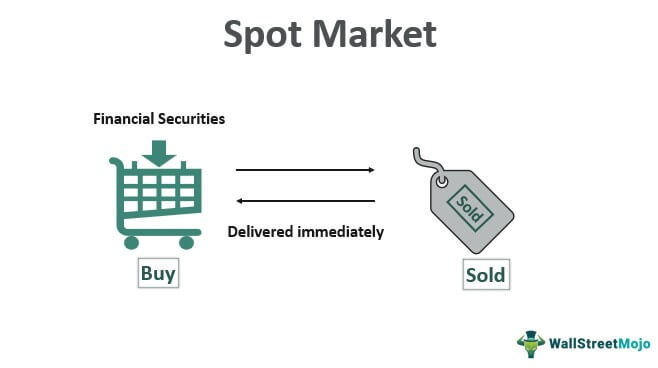
Focus: Immediate Delivery
Settlement: Typically within two business days.
Description: This is the most common market for retail traders. When you buy or sell a currency pair in the spot market, you’re essentially exchanging currencies at the current exchange rate for near-immediate delivery.
Example: You buy EUR/USD (Euro vs. US Dollar) in the spot market, expecting the Euro to strengthen against the Dollar. You’ll receive Euros within two business days, hoping to sell them later for a profit if the exchange rate moves in your favor.
2. Forward Forex Market:
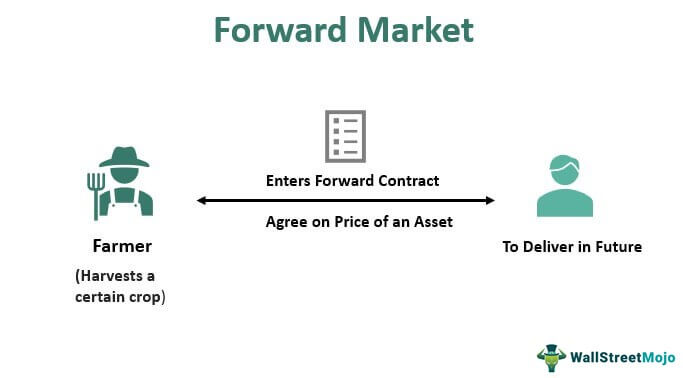
Focus: Future Delivery
Description: In the forwards market, traders enter into customized contracts to buy or sell currencies at a predetermined exchange rate on a specific future date. This market is primarily used by businesses to hedge against foreign exchange risk associated with future international transactions.
Key Differences from Spot Market:
Customization: Unlike the standardized spot market, forwards contracts allow for flexibility in terms of trade size, delivery date, and exchange rate.
No Immediate Exchange: No currencies are exchanged when the forward contract is initiated. The exchange happens on the agreed future date as per the terms of the contract.
Lower Liquidity: The forwards market is less liquid compared to the spot market due to its customized nature. There’s a smaller pool of potential counterparties for your specific contract terms.
Counterparty Risk: There’s a risk that the other party to the contract may default on their obligation to deliver the currency on the agreed date.
Choosing Between Spot and Forward Markets:
Spot Market: Ideal for short-term speculation on currency movements or immediate foreign exchange needs.
Forward Market: Suitable for businesses seeking to hedge foreign exchange risk for future international transactions.
Remember, the forwards market offers more flexibility but comes with lower liquidity and counterparty risk. Choose the futures market and type that aligns best with your trading goals and risk tolerance.
How Forex Trades Are Quoted (pips)
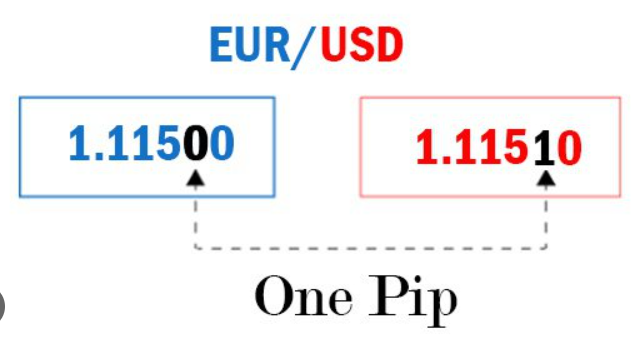
Pip stands for “percentage in point” and represents the smallest price change for most major currency pairs used. In simpler terms, it’s the fourth decimal place in a quoted exchange rate. For example, a pip in EUR/USD (Euro vs. US Dollar) is equal to 0.0001 (one-hundredth of a cent).
Why are Pips Important?
Forex futures markets can experience constant fluctuations, and pips provide a standardized way to track these minute movements. This allows traders to:
Measure Profit and Loss: Since profits and losses in forex trading are based on changes in exchange rates, pips help calculate the exact size of your gains or losses on a trade.
Compare Currency Pairs: Pips enable you to compare price movements across different currency pairs, even though their base currencies might have different values.
Manage Risk: By understanding pip values, you can calculate the potential impact of price movements on your trading capital and manage risk effectively.
How to Calculate the Value of a Pip:
The value of a pip depends on the specific currency pair you’re trading. Here’s the formula:
Pip Value = 1 pip (0.0001) / Exchange Rate of the Currency Pair
For instance, if the EUR/USD exchange rate is 1.2000, the value of one pip would be:
Pip Value = 0.0001 / 1.2000 = $0.00008333 (approximately)
Remember:
The Japanese Yen (JPY) is an exception. JPY pairs are typically quoted to two decimal places, so one pip in USD/JPY would be 0.01.
Some brokers offer fractional pips, also called “points” or “pipettes.” These represent movements even smaller than a standard pip.
By understanding pips and their role in forex quotes, you gain a powerful tool for navigating the exciting world of currency trading.
Getting Started (Without Investment)

To begin trading on the Forex market without making any initial investment, there are several strategies and opportunities available that can help you kickstart your forex trading platform and journey. Here is a comprehensive guide on how to get started:
Forex No-Deposit Bonuses
Brokers often offer small amounts of capital (ranging from $5 to $100) as bonuses to attract new traders. These no-deposit bonuses allow you to practice trading with real money without risking your own funds.

Pros:
Practice Trading: Allows traders to practice trading with real money without risking their own funds.
Cons:
Conditions: Often come with conditions such as trading volume requirements and withdrawal restrictions.
Forex Demo Contests

Participating in demo contests with virtual funds provides an opportunity to hone your trading skills and potentially win cash prizes. While you won’t earn real money directly, these contests are valuable for skill development.
Pros:
Skill Development: Provides an opportunity to hone trading skills and potentially win cash prizes.
Cons:
Limited Winnings: The winnings are usually limited, and transitioning to a live trading account is necessary to earn real profits.
Forex Proprietary Firms

Some prop firms, offer traders the chance to trade their capital without risking their own. By meeting specific criteria, traders can access substantial funding (up to $50,000) for a subscription fee.
Pros:
Access to Capital: Offers traders the chance to trade substantial funding without risking personal funds.
Cons:
Subscription Fee: Requires a subscription fee to access the funding provided by proprietary firms.
Trading Jobs

Getting a trading job at a financial institution or proprietary trading firm can provide a base salary and a share of the profits generated. However, landing such a job can be competitive and requires a strong educational background.
Pros:
Base Salary: Provides a base salary and a share of the profits generated for traders.
Cons:
Competitive: Landing a trading job can be highly competitive and demands a strong educational background.
Forex Affiliate Programs

By referring new forex traders to Forex brokers, you can earn commissions from their trading activities. This method allows you to enter the market without personal funds and can be lucrative if you attract active traders.
Pros:
Commission Earnings: Allows traders to earn commissions from the trading activities of referred new traders.
Cons:
Dependence on Referrals: Success in earning commissions is dependent on attracting active traders to the Forex brokers.
Steps to Consider Before Live Trading in Forex
Before venturing into live trading in the Forex market, there are essential steps and factors to consider to ensure a smooth and informed trading experience. Here is a comprehensive guide on the key aspects to address before engaging in live forex trading platforms:
Factors To Consider When Opening a Forex Account
Regulation: Ensure the broker you choose is regulated by a reputable authority. Regulation provides a level of security and protection for your funds.
Fees: Research and understand the fee structure of the broker, including spreads, commissions, and any additional charges for services like withdrawals or account inactivity.
Choose a Broker

Reputation: Select a broker with a solid reputation in the industry. Look for reviews, ratings, and feedback from other traders to gauge the broker’s reliability.
Offerings: Consider the broker’s offerings, including trading platforms, customer support, available trading instruments, and the types of accounts they provide.
Build a Trading Plan

Define Your Goals: Clearly outline your trading goals, whether it’s short-term gains, long-term investments, or passive income through trading.
Risk Management: Develop a risk management strategy that includes setting stop-loss orders, determining position sizes based on risk tolerance, and avoiding over-leveraging.
Trading Strategy: Establish a trading strategy that aligns with your goals and risk tolerance. This could involve technical analysis, fundamental analysis, or a combination of both.
Demo Trading: Practice with a demo account to test your strategies and familiarize yourself with the trading platform before transitioning to live trading.
Start Small: When transitioning to live trading, start with a small amount of capital to minimize risk while gaining real trading experience.
By following these steps and considering these factors, you can set a solid foundation for your live trading journey in the Forex market. Remember that thorough research, risk management, and a well-defined trading plan are key elements for success in the dynamic world of Forex trading.
Learning Platform & Practice
Selecting the right trading platform is crucial for your success in the Forex market. Consider factors like user-friendliness, available tools, reliability, and compatibility with your trading style.
Open a Demo Trading Account (with a Broker)
Select a Broker: Choose a reputable broker that offers demo accounts. Ensure the broker aligns with your trading needs and provides a realistic trading environment.
Register for a Demo Account: Sign up for a demo account with the broker of your choice. This account allows you to practice trading with virtual funds in real market conditions.
Forex trading example (using a demo account)
Step 1 – Currency Pair Selection: Choose a currency pair to trade, such as EUR/USD.
Step 2 – Analyze the Market: Use technical and/or fundamental analysis to assess the market conditions.
Step 3 – Place a Trade: Decide whether to buy (long) or sell (short) based on your analysis.
Step 4 – Set Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels: Manage risk by setting stop-loss and take-profit orders.
Step 5 – Monitor and Manage Your Trade: Watch how the trade unfolds and make adjustments if necessary.
Executing Trades (When Ready)
Now that you’ve gained a solid foundation in forex basics, let’s explore the practical steps of executing trades (using a demo account, of course!). Remember, this is a simulated environment where you can hone your skills without risking real money.
1. Pick Your Size and Position:
Trade Size: This refers to the amount of currency you’re buying or selling in a trade. It’s crucial to start trading small on a demo account to get comfortable with managing positions. Most platforms allow you to trade in mini or micro lots (smaller units of currency) to minimize risk.
Long or Short Position: Recall from earlier lessons that you can go long (buy a currency pair, expecting the base currency to strengthen) or short (sell a currency pair, expecting the base currency to weaken).
2. Open Your First Position (Practice Makes Perfect):
Analyze the Market: Before diving in, analyze market conditions using technical indicators or fundamental analysis (learned from educational resources). This helps you make informed decisions about entry and exit points.
Place an Order: Once you have a forex trading strategy in mind, use your forex broker’s platform to place an order. Specify the currency pair, trade size (amount), and order type (market order for immediate execution or limit order for execution at a specific price).
3. Monitor Your Positions (Risk Management in Action):
Real-Time Tracking: Keep a close eye on your open positions using the platform’s live quotes and charts. Monitor how the exchange rate of your chosen currency pair fluctuates.
Stop-Loss Orders: Forex trading involves inherent risk. To limit potential losses, consider placing stop-loss orders. These automatic orders close your position if the price moves against you, reaching a predetermined level. Demo accounts allow you to experiment with stop-loss placement without real consequences.
Take Profit Orders: You can also set take-profit orders to automatically close your position when the price reaches a desired profit target.
4. Close Your Trade (Practice Makes Perfect):
Manually Closing: You can manually close your open positions at any time by placing an opposing order (selling if you bought earlier or buying if you sold earlier). Monitor market movements and close your position when your strategy dictates, aiming for a more profitable trade outcome (remember, this is a demo, so there’s no real profit or loss).
Order Fills: Pay attention to order fills. Sometimes, market conditions might prevent your order from being executed at the exact price you specified.
Remember: Executing trades on a demo account is all about practice. The more you experiment with different order types, position sizing, and risk management techniques, the more comfortable you’ll become when you transition to live trading. Treat your demo account as a learning lab to refine your forex trading skills.
For better trading success, visit our site. Find detailed reviews of forex trading firms and stay informed on the latest prop trading news. Unleash your trading skills with us!










